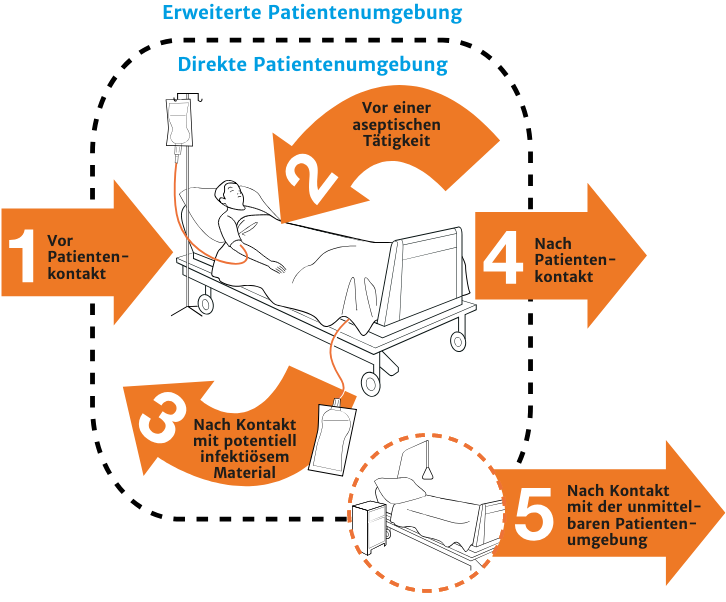
Moments for Hand Hygiene
The Indications
An indication is defined as a situation in which hand hygiene is necessary, in other words where the risk of transmission of a pathogen exists. Hand hygiene effectively prevents such a transmission.
An indication is designated BEFORE contact or AFTER contact, which nonetheless should not necessarily be considered as the beginning or end of a medical sequence or activity. It is defined as movements between various areas (the direct and expanded patient environment, colonized or not colonized parts of the body).
The indications for hand disinfection correspond to clear situations in the normal course of patient care. Given the number of possible situations, a program has been created by WHO (World Health Organization) which is broken down into five indication groups:
- BEFORE contact with patient
- BEFORE aseptic activities
- AFTER contact with possibly infectious material
- AFTER contact with patient
- AFTER contact with a patient’s direct environment
This model can be utilized in all areas of healthcare and is a useful aid for staff in recognizing situations clearly. Its content corresponds to the Robert Koch Institute’s guidelines for hand hygiene.
Why
To protect the patient from colonization by pathogens which may be temporarily present on the hands of staff
WHO Recommendation
- BEFORE direct contact with a patient, i.e. direct bodily contact (Category IB)
Why
To protect the patient from the transmission of potential pathogens, including pathogens from the patient’s own body, to sterile / not colonized parts of the body.
WHO Recommendation
- BEFORE the connection or disconnection of an invasive device regardless whether gloves are being worn (Category IB)*
- When moving between colonized / contaminated and clean parts of the body in the course of patient care (Category IB)*
Why
To protect staff and the expanded patient environment, including future patients, from potential pathogenic agents
WHO Recommendation
- AFTER contact with bodily fluids and excretions, with mucous membranes, skin that is not intact, and bandages (Category IA)*
- When moving between colonized / contaminated and clean parts of the body in the course of patient care (Category IB)*
- AFTER removing gloves (Category IB)*
Why
To protect staff and the expanded patient environment, including future patients, from potential pathogenic agents
WHO Recommendation
- AFTER direct contact with a patient, i.e. direct bodily contact (Category IB) *
- AFTER removing gloves (Category IB)*
Why
To protect staff and the expanded patient environment, including future patients, from potential pathogens.
WHO Recommendation
- AFTER contact with surfaces and medical devices in the patient’s immediate environment (Category IB)*
- AFTER removing gloves (Category IB)*
* These categories reflect the degree of evidence that support these recommendations.
| Category IA: This recommendation is based on well conceived systematic reviews or individual high quality randomized controlled studies. | Category IB: This category is based on clinical or high quality epidemiological studies and rigorous and plausible theoretical conclusions. |
The model provides a definition of a direct and an expanded patient environment:
The direct patient environment is defined as:
- On intensive stations: the patient bed with Infusomats/Perfusors, ventilators, monitoring console and its accompanying computer station (if it is located directly next to the patient’s bed), as well as all devices assigned to the patient.
- On normal wards: patient bed with nightstand and the patient’s personal belongings there, as well as all devices assigned to the patient.
All other areas of the patient’s room.